World Class Faculty & Resources
The Duke Medical Physics Graduate Program is unique in many regards. We have a world class faculty, amazing institution resources, generous program facilities, and we live in a great part of the country. Let’s learn more about each in turn.
Program Facilities
Our CAMPEP-accredited program is one of the few that equally emphasizes all four major areas of medical physics: diagnostic imaging, nuclear medicine, medical health physics, and radiation therapy.
In addition to our diverse list of courses, we also offer an optional summer clinical internship for MS students interested in additional clinical training. The Medical Physics Program itself has 5,000 square feet in Hock Plaza (see picture below) containing an expandable classroom, a dedicated laboratory, multiple areas for group and individual study, administrative offices, and a kitchen.
Existing equipment in the Medical Physics Program laboratory includes radiation protection lab equipment (whole body counter, high resolution germanium gamma detector, liquid scintillation counter), dedicated equipment for radiation dosimetry, and a stand-alone gamma camera scanner. Finally, there are two Eclipse workstations donated by Varian for the exclusive educational use of our students.

Institution Resources
The Program draws upon the resources of one of the best medical centers and universities in the United States. This translates into cutting-edge facilities for education, research, and clinical training. In the past decade, Duke Medicine opened 3 major new buildings totalling over 900,000 square feet at a cost of nearly US$900 million: Trent Semans Center for Health Education, Duke Cancer Center (see pictures below), and Duke Medicine Pavillion.
The hospital and these new buildings are home to radiology and radiation oncology, which are major contributors to our program. Together, those departments operate an abundance of diagnostic imaging equipment including MRI, CT, and molecular imaging with PET-CT, SPECT, and SPECT-CT. Additionally, radiation oncology has an array of state-of-the-art linear accelerators capable of performing intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), volumetric modulated radiation therapy (VMAT), image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), total body irradiation (TBI) and total skin irradiation (TSI).
There is a dedicated brachytherapy suite which allows real-time administration and CT/MR guidance of both low-dose-rate and high-dose-rate brachytherapy. Medical Health Physics oversees and regulates radiation use throughout the medical center as well as the university, including the Triangle Universities Nuclear Laboratory and Duke Free Electron Laser Laboratory.
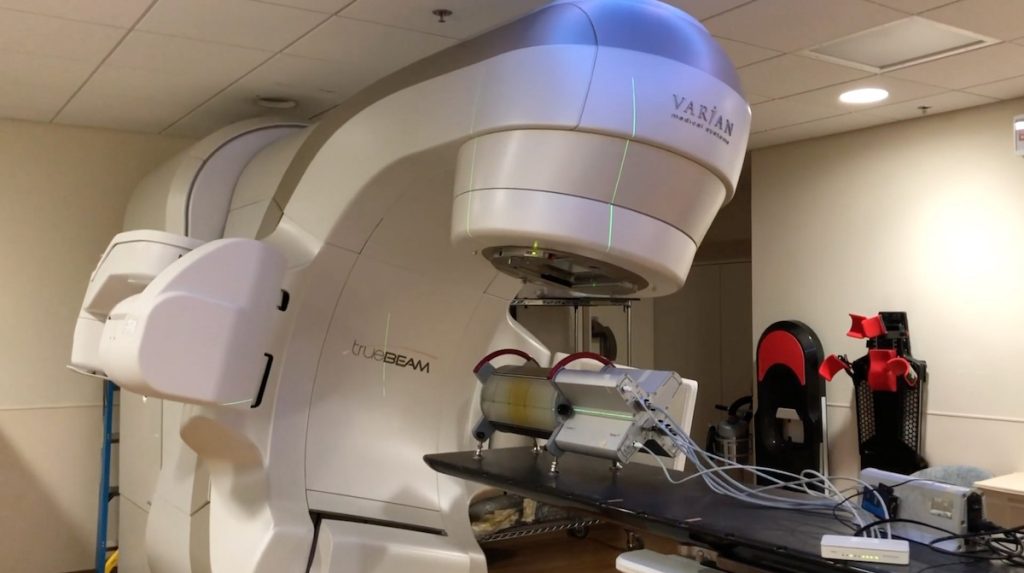
Existing Equipment and Facilities Include:
- 8 clinical radiation oncology treatment systems including TrueBeam and EDGE to perform intensity modulated radiation therapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and stereotactic body radiation therapy;
- Brachytherapy (low dose rate, high dose rate, eye plaque)
- 35 clinical CT scanners including photon-counting CT (among first in US, installed during pre-FDA approval phase)
- 20 clinical MR scanners
- 2 PET/CT scanners in nuclear medicine cameras with 9 gamma cameras;
- Center for Virtual Imaging Trials, creator of XCAT human computational models licensed by 400+ research groups, also home to Carl E. Ravin Advanced Imaging Laboratories
- Center for In Vivo Microscopy with 7.0T and 9.4T preclinical MRI systems
- Duke Center for Artificial Intelligence in Radiology
- Duke Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Center
- Positron Imaging Research Lab with dedicated research PET/CT scanner, PET cyclotron, and radiopharmacy
- Xenon MRI Shared Resource with 129Xe hyperpolarizers, a newly FDA approved imaging technology developed and commercialized at Duke
- Radiation Dosimetry Laboratory
- Radiochemistry laboratories for monoclonal antibody imaging and therapy;
- Duke-UNC Brain Imaging and Analysis Center and Center for Advanced Magnetic Resonance Development with 3 dedicated research 3T MR scanners;
- Ultrasound laboratories in biomedical engineering.